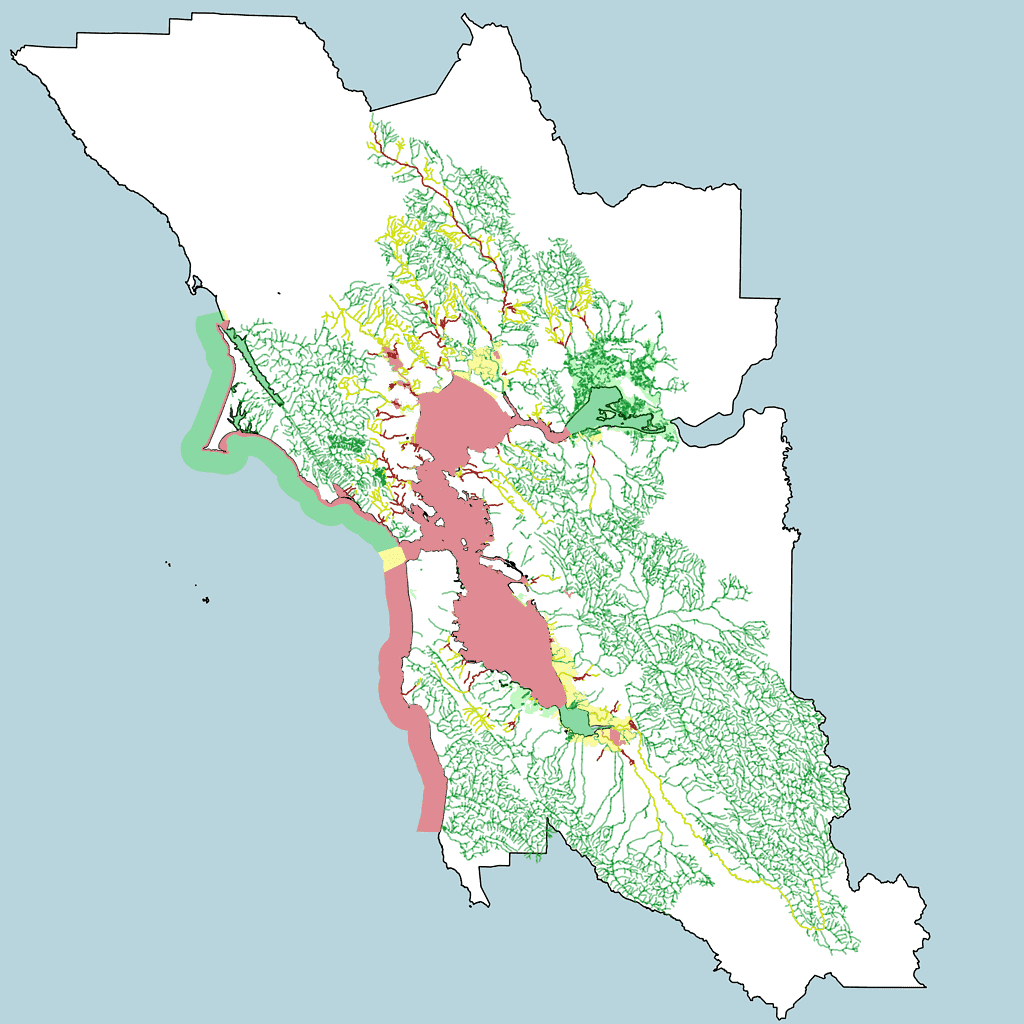
From the beginning of my life, I never had the opportunity to learn about my culture, or where I was from. For the first 12 years of my life, I never even saw another Paiute person.
This was because I was adopted at birth. I knew that I was Native American. That I should be on a reservation somewhere in Central California. But, instead, I found myself in Alameda; trying to navigate the expectations and life plans set by my new, white, parents.
This kind of estrangement is common.
It comes in many different forms, for many different reasons. Boarding schools are pointed to, most often. But cultural estrangement started in California with the Mission System. It continued on through Mexican Occupation, when the missions were secularized, and “Spanish” land was granted to Mexican citizens, and select Indigenous People, who were associated with the Missions as ranchers and herders, or were deeded land in some other way. This was actually the first Native American “buy-in” that occurred in California.
When the American government came in, their imperative was to destroy or pacify people who they viewed as “savage”, and sub-human. Giving land to these people who Americans found so hard to wipe off the face of the planet was unheard of. All land, property, and wealth held by the First Californians were immediately seized, destroyed, or transferred to white interlopers.
Some Native Americans went into hiding. Claimed to be Spanish. (They already spoke Spanish.) …Leaned into their baptismal names.
This was the second estrangement.
American Occupation came with a number of different attempts to destroy, pacify, and ultimately assimilate and “breed out the savage”. Each of these attempts divided (and sub-divided) tribal groups; moved us farther and farther away from our homelands, each other, and purposely tried to destroy everything linking us to the old ways. This was a sophisticated attempt at genocide, and population control; and people need to stop minimizing effects of this recent history on Indigenous People in America, today.
Native American People have been forced to live as Prisoners of War since the 17th Century. For more than three centuries, Indian Children and Infants were taken from their families, and placed into Missions, Orphanages, Boarding Schools, and worse. For most of the 19th and 20th centuries, it was legal for White Women to take Indian Children away from their families, and keep them as “wards”. [Like in the series “Them”.]
So it’s not uncommon for a Native American Person to be so estranged from their family and culture. To have such a conflicted self-image of what it means to be Native American, and what Native American really is. For Spanglish to be spoken on the rez out here, in California. For former “Mission Indians” to be so heavily involved in the Catholic Church, and the veneration of the Missions.
But what if a Native American Descendant from California doesn’t want to go to the Catholic or Mormon church to find out about their own people?
What if they’re tired of listening to a narrative from white people’s perspective? From the Eastern U.S. perspective of tribes like Dine, Lakota, Sioux? From the perspective of people who view Native America as a homogeneous group?
Where does someone go to find the stories of their specific tribe? The songs of the place they come from? Pictures of their ancestors? The history of their reservation? Where their ancestors lived before that?
Where do you go when your only sources are generic, pan-Indian narratives, and single-page, one-sentence mentions of your tribe?
I decided to search historic newspapers, museums, government, and institutional records.
Historic Newspapers are hard to locate. And even harder to read for free. Many of these newspapers were taken out of circulation, and stored on microfilm. Even more are locked behind Ancestry.com (and affiliate) pay gates, specifically. It is interesting to note that “Ancestry” is based in Salt Lake City, Utah, though.
Museums store items by the Date Received; not by Keyword, or Subject–which shows that Museums have historically been about accounting and fundraising more than they were about collecting items which they intend to reference, much less curate. This makes the situation even more problematic, because researchers are expected to do the work of tracking something down, and often times creating a new library information system in the process. [Basically, re-cataloging every single object to find the two or three that were actually being sought after.]
The amount of free labor some museums get on the backs of unpaid researchers is very disproportionate to the amount of useful information researchers actually find when laboring for said museums.
Government Records only had to be stored for a certain period of time. Certainly, anything more than 100 years old was more likely to be destroyed, than it was preserved. Much of the City of Alameda records were converted to microfilm; combined with transcriptions of the Official Alameda Newspaper of Record, then simply labeled “Historic Rolls”.
Much of these rolls contained little to no useful information, and was simply a transcribed duplicate of several newspaper reels, which were also available. Still, missing records stymied my search. It almost seemed as if things were intentionally removed from the City of Alameda Historical Record between 1910, and 1960.
Other cities which were consulted, like Pleasanton, San Leandro, and Hayward, do not have historic newspapers from before the early 1900’s. These inquiries were usually passed on to local museums. Then on to local genealogical and historic societies–where the inquiry usually died. This is to say that there are no contrasting reports available from other historical newspapers (yet.)
Governmental Chain of Custody
Furthermore, because of the changeover from Spanish, to Mexican, to American hands: the chain of custody of important documents was broken each time the land changed hands. The U.S. Government was not interested in keeping prior records[; which also explains the fundamental lack of understanding of tribal cultures American anthropologists still experience to this day.]
This is why the “California Land Grants” case happened, in 1851. Because rich Mexicans (and Spanish ex-pats) were getting jilted out of their land they had old titles to, by white people, who claimed their American land deed superseded any other. (I mean, this is consistent with the U.S. policy of west-ward expansion during the late 1800’s, to test Mexico’s control over ‘The West’, and eventually gain control of California–among other territories.)
Mission/Spanish/Mexican records are still somewhat of a mystery and records were basically abandoned “as the vine withered”.
This is because many of the missions and forts Spain installed in California were actually remote forward operating bases.
Paperwork flowed back through California, to Mexico, and over the Atlantic Ocean, to Spain–when everything was working as planned. This organization was already broken down by “Corporate Office”, “Regional Managers”, “District Managers”, “Store Managers”, “Shift Managers”, and Baristas.
So, when the Spanish were sent back to Spain, those documents stayed here, were hastily mailed out, or were destroyed.
When the Missions were secularized, those documents were abandoned, taken by cardinals (or whoever), or destroyed.
Anything that wasn’t specifically removed and preserved was probably destroyed in the [totally righteous] fires that destroyed many of the the San Francisco Bay Area Catholic Missions the first time.
So, when it comes time to track down the records of these organizations; it’s necessary to chase them all the way back to the original departments and agencies which created them. This search almost always leads to institutions like the University of California, at Berkeley.
Why? Because, it turns out, the University of Berkeley Phoebe A. Hearst Museum of Anthropology, and the U.C. Berkeley Library has the largest collection of relevant materials within 50 miles.
Institutional Records and Academic Studies
Academic Institutions, like The Smithsonian, and the University of California, made their names on robbing the graves of Native American and Indigenous People all around the world.
Thousands upon thousands of bones, and cultural artifacts are in the custody of these institutions, waiting to be returned to their descendants, and laid to rest in the manner of each of their hundreds of individual tribes. More than half of the remains are “tribally unaffiliated”; and stay in limbo, because they have no living descendant to receive them, and no ancestral land to be laid to rest in.
The “researchers” who did this physically separated people from their final resting places, mixed and miss-matched parts of other people’s bodies together, failed to properly label our ancestors, and now have what amounts to a “spare parts bin” of archaeological malfeasance.
As much as Archaeologists and Anthropologists would like you to believe the opposite, these bones were found by systematically cutting open cemeteries, and removing rows of bodies under the guise of “legitimate scientific research”.
They did this all the while wondering, “Where did these people disappear to?”
Knowing full well that Indian Wars were raging nearby.
Conflicts such as:
Sioux Wars – 1854-1891 in the Great Plains
Ute Wars – 1850-1923 in Utah
Apache Wars – 1854-1924 in the South-West
They wondered…
Even with the knowledge that an Indian Reservation or Indian Town existed within 100 miles of any place mentioned in any anthropological or archaeological study/survey from 1860-1920.
These “ethnologists”, anthropologists and archaeologists were living through the California Land Grant Cases.
Anybody in the business of “antiquity” should well know the whereabouts and disposition of any of the Indigenous People whose graves, bones, and property they were “studying”, or auctioning off to private collectors.
Especially when the battles were making front page news daily.
There is no answer for this willful ignorance, and unethical exclusion of important facts and datum. The narrative of Native American History, as told by colonizers, is full of these types of falsities, and lies by omission. And things like this really call to question the accuracy, and reliability of any of these works.
If you can even get access to them.
Institutional Gatekeeping of Tribally Affiliated Knowledge/Artifacts
Because Universities, Museums, and other Grave Robbers (“hunters of antiquities”, “tomb raiders”, etc.)–as well as Ethnologists, Linguists, and Archaeologists–stole bodies; sacred, ceremonial, and cultural artifacts; caused the damage and loss of cultural land and sites; and attributed Native American intellectual property to themselves, instead of to the Native American creators of said property;
And,
Because of the sustained and forceful objections to the theft and kidnapping of Native American Bodies and Culture by Native Americans, and The Public; as well as demands for the return of Native American Remains and Items & Artifacts:
The Native American Graves Repatriation Act was enacted Federally, and by the State of California to protect the Graves, Remains, Cultural Sites, Artifacts, and Other Native American Objects within the State; as well as to create a framework for the repatriation of Native American remains in the possession of Universities and Institutions.
The Native American Heritage Commission was created in California to directly administer these efforts. In 1982, the Commission was authorized to make a determination of “Most Likely Descendant” when Native American remains are found. Most Likely Descendants are people or tribal groups who have documented ties to the land where Native American Graves were disturbed, and Native American bodies have been found. The Native American Heritage Commission is charged with assisting Tribal Notification, and the process of Tribal Consultation by the Most Likely Descendants.
The tribal consultation process only offers two ways to “mitigate” the damage to Native American Graves, Remains, Landmarks, Objects, and/or other Funerary Things:
- Re-bury the remains in a place where they will not be disturbed;
- Remove the remains, and return them to the Most Likely Descendant for proper burial.
The process of notification goes something like this:
- Human remains found, notification to Coroner.
- Coroner determines remains are Native American, and therefore under the jurisdiction of the California Native American Heritage Commission (CalNAHC).
- CalNAHC provides a notification list to property owner. This list contains the contact information for Tribal Groups who are Most Likely Descendant(s) of the Native American body found.
- Tribal Group is notified and only has a certain amount of time to make a response as to how the Native American remains should be treated, or how a project can avoid disturbing cultural resources.
If the Tribe does not respond within 30 days of notice, the developer or property owner will be able to continue work, unencumbered by the Native American Graves Protection Repatriation Act. And, in the case of housing development, the building process will be allowed to be streamlined, via AB 831, an act relating to housing, and declaring the urgency thereof.
But, if the Most Likely Descendant and Property Owner are not able to reach a compromise….
Say the MLD wants absolutely no more development of the land; and the property owner (CalTrans, Ruegg & Ellsworth, San Rafael Rock Quarry, etc.) is unable to reach a compromise, the desecration will be allowed to continue if the developer simply alleges they tried their best. The construction just won’t be “streamlined”, and will have to go through the normal Environmental Assessment procedure; and will likely still result in the destruction or desecration of Tribal Cultural Resources.
The aforementioned refers to situations where Native American Graves and/or Remains (funerary objects, etc.) have been found.
CalNAHC also plays a role when Public Entities, like Caltrans, Amtrak, Los Angeles Public Works, East Bay Municipal Utility District, East Bay Recreation and Parks Department, the City of Menlo Park, etc., want to develop anything on what’s considered “public land” or subsidized by public funds.
We’re talking: Public Works Projects, Improvement Projects…. Things which translate into freeway on or off-ramps, giant rain water caches underneath Glen Cove Park (in Vallejo, California), water pumps in Alameda, Treasure Island, San Francisco… BART stations, Water Treatment Plants… And more.
All of these places around us started as project proposals.
And each proposal needs to comply with local, state, and federal law. Each facility, site, or subject property–after being built–needs to operate in compliance with local state, and federal law.
Namely: CEQA. The California Environmental Quality Act.
CEQA was one of the first set of laws that recognized Native American Graves, Objects, etc., as being valuable, and worth saving.
Because of CEQA, when these proposed public works projects, projects on public land, or projects using public money, are submitted, they are also required to perform an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA).
You’ve probably seen the Public Notice of Hearing(s) that are posted on the front of buildings, or on the fences outside of where buildings once stood.
These are Required Notices to The Public. You. These hearings decide the very fate of the sacred places which have, up to this point, become Shopping Malls, and Subdivisions with Waterside Parks.
These Notices tell you when a Water Treatment Plant, Waste Management Facility, Shooting Range, or Quarrying Operation has an upcoming Permit Hearing.
In fact, multi-year operations, like the San Rafael Rock Quarry, are required to resubmit an Environmental Impact Report periodically, and submit to a public hearing (to the County Board of Supervisors, in this case), to keep their permits, and continue operating.
These EIA’s are often very long (more than 40 pages,) and contain a multitude of very technical information regarding the current state of the land intended to be “used”, and the speculative impact of the operations intended upon said land (e.g. pollution, destruction of natural habitat, etc.) The specifics change with every project. However, the demands of the Environmental Impact Assessment remain constant.
Recently, the passage of Assembly Bill 52 (Chapter 532, Statutes 2014) codified the inclusion of a single question regarding “Tribal Cultural Resources”:
Would the project cause a substantial adverse change in the significance of a tribal cultural resource, defined in Public Resources Code section 21074 as either a site, feature, place, cultural landscape that is geographically defined in terms of the size and scope of the landscape, sacred place, or object with cultural value to a California Native American tribe, and that is:
a) Listed or eligible for listing in the California Register of Historical Resources, or in a local register of historical resources as defined in Public Resources Code section 5020.1(k), or
b) A resource determined by the lead agency, in its discretion and supported by substantial evidence, to be significant pursuant to criteria set forth in subdivision (c) of Public Resources Code Section 5024.1. In applying the criteria set forth in subdivision (c) of Public Resources Code Section 5024.1, the lead agency shall consider the significance of the resource to a California Native American tribe.”
Because of this, the California Native American Heritage Commission is charged with yet another duty: maintaining a Tribal Contact List for CEQA Purposes, per AB 52 (CA PRC §21080.3.1…); and when Cities and Municipalities create their General Plan [among other things], per SB 18 (CA GOV §65352.3).
The California Native American Graves Protection Repatriation Act, and the authoritative statutes empowering the California Native American Heritage Commission, specifically state the importance of the “confidentiality of information regarding specific identity, location, character, and use of those [Native American] places, features, and objects.”
In the courts, this has often played out as the misreading of statute from “confidential” to “secret”. However, statutes surrounding the confidentiality of Native American (Tribal) Cultural Resources simply state that NAHC is “not required” to disclose certain records, or information specifically enumerated in the California Government, and Health & Safety Codes.
The statutory scheme, as it stands:
requires Tribal Cultural Assets to be listed (in a confidential appendix) in Environmental Impact Assessments. The specific information regarding the Tribal Cultural Resource is hidden. But general, non-confidential information regarding the Existence Of A Tribal Cultural Resource that could be significantly effected by a proposed project should be published and made available to the general public. [PRC §21082.3(f)]
These public sections of the Proposed Environment Impact Report, or Proposed Negative Impact (“Declaration”), which mentions “Tribal Cultural Resources”, will be small. Maybe the heading won’t even catch your eye. And the “general information” presented on the document will minimize the existence of Tribal Cultural Resources, even though the report is supposed to clarify how significantly the Tribal Cultural Resource will be affected.
In fact, the EIR, or Negative Impact Declaration, is supposed to tell you how damage to Tribal Cultural Resources could have been mitigated, or the circumstances behind why the destruction of Tribal Cultural Resources was “unavoidable”. It should say whether or not Tribal Consultation (or “Scoping Activities”) were conducted or concluded, or if an agreement was reached with the direct Lineal, or Most Likely Descendants of the Tribal Cultural Resource.
The EIR, or Negative Impact Declaration should make it clear whether or not the tribe even responded to invitations for consultation. That information should be in bold. But it’s not. And, who actually knows how to read an Environmental Impact Report?
At some point, we have to realize that our ignorance is being taken advantage of every day.
The fact that we are distracted every single waking second is an advantage that is being leveraged against us in the long wars of attrition against corporations and governments who want nothing more than to exploit our land, and tear the bodies of our ancestors out of the ground to build condos that cost $1.5-2M, each.
This is why property owners refuse to register Native American Historical Sites. Because this land is worth more money than many of the people who live on it will see in our entire lives. This land is worth more than us. And erasing us, or creating a statutory scheme that makes it easy to disregard Native American objections to the desecration and theft of our land, also makes money for themselves while they do it.
This is a Billion dollar industry that Native American “Consultants” are sucking the dew off of in only the most parasitic, “bottom-feeder” kind of way. The disrespect to the bodies of our elders. Our great grandparents…. It’s all just for the zero’s.
No matter how the statute is written. No matter how much commitment legislators and politicians can claim to have, the easy-out that Developers and Governmental Agencies has hinges upon the responsibility of a Tribal Organization to respond to these “invitations” for tribal “scoping” and “consultation”.
The statute presupposes that Government Agencies and Developers are law-abiding. But, when it comes to the required “consultation” with Native American Tribes, Lineal, or Most Likely Descendants… all of the exceptions hinge upon the “nonparticipation” of Native Americans.
(d) In addition to other provisions of this division, the lead agency may certify an environmental impact report or adopt a mitigated negative declaration for a project with a significant impact on an identified tribal cultural resource only if one of the following occurs:
(1) The consultation process between the California Native American tribe and the lead agency has occurred as provided in Sections 21080.3.1 and 21080.3.2 and concluded [in an agreement with Tribal Consultants.]
(2) The California Native American tribe has requested consultation pursuant to Section 21080.3.1 and has failed to provide comments to the lead agency, or otherwise failed to engage, in the consultation process.
(3) The lead agency has complied with subdivision (d) of Section 21080.3.1 and the California Native American tribe has failed to request consultation within 30 days.
Assembly Bill 52
According to Assembly Bill 831, housing projects meeting the above criteria would still be “streamlined”, removing most of the public response and permit hurdles necessary for quick development.
The problem is that Native American Graves, Cemeteries, Cultural Sites, and Sacred Lands are still being given the green-light for demolition.
They are being rubber-stamped for desecration by a function of law that simply added Notification, and “Due Process” instead of actual Justice, and Accountability.
There must be a way to advocate for Native American Tribal Cultural Resources, like Graves, Cemeteries, and Sacred Places, when Lead Agencies and Private Developers receive no response through the Tribal Contact List.
Either the Native American Heritage Commission must step up for all of these places, or they need to devise an apparatus that will allow true conservation work (the very basis of NAHC’s Mission) to take place without them.
Stay tuned for more.