
Fully updated, featuring new historic wetlands, shorelines, and more.
Available exclusively at the Alameda Native History Project.
Find it on our website:
NativeHistoryProject.org > Maps > Alameda Shellmounds Web Map
All juxtaposed against the modern day landscape to provide accurate scale and positioning.
Available in several sizes.

Because of the juxtaposition of the historic peninsula with it’s present day silhouette, it is much easier to see which parts of Alameda were physically connected and formed the peninsula more recently known as the “Encinal”.
Both Alameda and Oakland are in a region referred to as Xučyun (also known as “Huchiun”.) Xučyun is part of the ancestral homeland of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area. Muwekma have lived in the Bay Area for over 10,000 years.
For the first time, all four of the Alameda Shellmounds have been put onto one map. Most people only know about the shellmound on Mound Street. But there are more shellmounds, in Alameda. There were over 425 shellmounds in the Bay Area. Including Alameda’s largest shellmound, at the foot Chestnut.
See also: Shellmounds – What Are Shellmounds?
This place we call Alameda was once called “La Bolsa de Encinal”. Meaning, “the Encinal forest”. Because the peninsula was host to a verdant, “ancient”, Live Oak forest. (The forest still exists. It just looks different.)
Many of the first accounts of the historic peninsula use rather idyllic, and paradisaic language to describe the rich pre-contact ecosystem that thrived here.
Alameda was once referred to as a “Garden City”. This is the place where the Loganberry was supposedly born.
tl;dr : Everyone wants to know where the landfill is. [There! I said it, okay?] They don’t even really care where Alameda used to be connected to Oakland. Or about the ancient whirl pool in la bahia de san leandro. But, whatever.
Look closer, and you can see the footprints of present day buildings. That’s the landfill.
For real though, I made this layer using pre-1900 shoreline vector data I compiled for the Bay Area region, and stitched together.
In Version 1, I made a kind of sloppy polygon with historical shoreline vectors, and painted it green. It was a good placeholder for the historic marshes and wetlands of the Bay Area.
Version 2 features the finely detailed historic wetlands layer created for the Bay Area Shellmounds Maps. It features very precise cut-outs for historic creeks, channels and waterways; and features full-coverage of the Bay Area region.
If you want some actual historical eco-data, check out the San Francisco Estuary Institute. They have some brilliant historical ecology GIS you would probably love, if you’ve read this far.
The Alameda Shellmound Map, Version 2, is ground-breaking in its completeness and exquisite detail.
Printed in vivid color, on premium paper. Purchase through the Alameda Shellmounds Map square payment link. 10% of all proceeds from Alameda Shellmounds Map sales go to the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area.

[Footnote: Imelda Merlin mentioned numerous shellmounds in her Geology Master Thesis, but none of her assertions were backed up with any relevant citations. And geology is not archaeology, ethnology, or anthropology, the areas of study that normally concern themselves with Tribal Cultural Resources like shellmounds.
Furthermore, the famous “Imelda Merlin Shellmound Map” was actually a map of Live Oak trees present in Alameda at the time Merlin wrote her thesis (in 1977).
The “Map of Whitcher’s Survey of ‘The Encinal’ in 1853. In Alameda City Hall.”, cited on page 104 of Merlin’s thesis, has never been found by Alameda City Hall, the Alameda Free Library, or the Alameda Museum.
Certainly this means Imelda Merlin has failed to meet the burden of proof required for institutions like Alameda Museum to take reliance upon her claims re: Whitcher’s Survey, and locations of any mounds. Yet, somehow, Merlin’s geology thesis was Alameda Museum’s sole reference regarding shellmounds. (For years Imelda Merlin’s geology thesis was viewed as the authoritative source of information about Alameda shellmounds.)]
One of the ways Alameda Native History Project decolonizes history is by interrogating the record. This means tracking down and reading citations. Critically evaluating reports and studies for bias. And calling out poor research, and prejudiced conclusions for what they are.
We decolonize history by updating the maps and diagrams of our past. Producing accurate, fact-based educational and reference materials to replace the biased and inaccurate educational products–which are still misinforming our schoolchildren and the greater public today.
By providing a more nuanced and comprehensive perspective; and doing away with the old, over-copied handouts from decades past: we are able to shed the misinformed, and racist, stereotypes and quackery that typify generations which brought us things like: “kill the indian, save the man”, Jim Crow, and “Separate But Equal”.
We vigorously challenge the cognitive dissonance of so many California Historians, asking “Where did all the Indians go?”, at a time when the entire United States had declared war on Native Americans. … Including the first Governor of California, who called for “war of extermination” against California Native Americans.
These ideas, stereotypes, attitudes, and beliefs have managed to propagate themselves time and time again in the textbooks and lesson plans used to “educate” countless generations of Americans.
👉🏼 Your purchase of the Alameda Shellmound Map supports our mission of decolonizing history. 🙌🏼

This is an excerpt of an email to the Indigenous Land Lab mailing list.
Collecting as much materials for Acorn Granary construction as possible.
There are other, more serious plants, like stinging nettle, which I would like to take the time and make some cordage from. Just like splitting the willow reeds to make strips for weaving the granaries.
Hard-to-find materials would be redwood bark–which would be nice to use on the outside of a granary. And then Pine Sap–which simply won’t be readily available until later, and will require some travel into higher elevations to gather.
If you would like to help gather more natural materials for Acorn Granary Construction, please sign up for the Indigenous Land Lab Email List, to help plan what dates and times work best to plan a meet-up to harvest materials.
You are invited to participate in any or all aspects of planning and working. We’re assuming tilling should happen sometime in August.
We’ve received a lot of interest, support, and some very generous donations of equipment, supplies, and money! (All donations are tax deductible!)
We managed to find a roto-tiller we can use when we’re ready!
Some of these things we know we can borrow, like a post driver. But other stuff–like shovels and rakes–we need to keep on hand.
Luckily, we don’t need a large amount of anything other than Silage Tarp, Chicken-Wire, and Compost.
Join us in harvesting Willow, Bay Leaf, and Nettle for granary construction.
Donate tools: If you have some tools, supplies, or equipment on this list, we can pick it up. If you have a truckload of compost, we can meet you at the land lab for a drop off.
Purchase directly from our wishlist. Indigenous Land Lab Wishlist is available here.
Donate to the Alameda Native History Project. Tax deductible donations can be made to the Alameda Native History Project here.
Alameda Native History Project is fiscally sponsored by The Hack Foundation (d.b.a. Hack Club), a 501(c)(3) nonprofit (EIN: 81-2908499). Any monetary donation, or donation in-kind is tax deductible, and you will receive a donation receipt whether you want it or not. LOL. I mean, if you say no, then we won’t, but who doesn’t like a small write-off?
Anyway, it’s Pride Week, so things are totally hectic as I volunteer for the Gay American Indians. Check out the attached fliers for GAI events. Consider marching with Gay American Indians at Pride!

Yours truly,
Gabriel Duncan
via collab@nativehistoryproject.org
To join the land lab, email collab@nativehistoryproject.org, or use the form below.
Indigenous Land Lab
Mailing List Sign-Up Form

There is land for a lab. With amazing potential. There are seeds. And water. We are ready to begin.
"All the flowers of all the tomorrows are in the seeds of today."What a great place to start. This is exciting.
Bring gloves, a hat, and your waiver. LOL. (No, for real, it’s for our fiscal sponsor.)
We’ll provide water, some shade, and (hopefully) lunch during official workdays. (At least snacks!)
https://forms.gle/zCe8ab5VnPwQDJYMA
The first, of course, would be by donating landscaping & gardening equipment you no longer use. But, we would be especially grateful for the use of your walk-behind “brush mower”, “brush hog” or “rotor cutter”.
The land we have is wild, and untamed. It’s overgrown with invasive grass, some hemlock, and a random shrub or two. This is why our list sounds more like a fire crew equipment list than what you’d expect for an established garden.
Alameda Native History Project donation link.
Alameda Native History Project is fiscally sponsored by The Hack Foundation (d.b.a. Hack Club), a 501(c)(3) nonprofit (EIN: 81-2908499). As such: all donations you make are tax deductible.
May 4th, 2024
11:00 AM to 2:00 PM
Corica Park Golf Course Clubhouse
1 Clubhouse Memorial Road, Alameda, CA 94502
Tickets: $15
-Limited Sponsorships Available-Proceeds from ticket sales go toward venue rental, lunch (and refreshments), future programming, and operations.
All donations are tax deductible.


We’d like to thank Greenway Golf, and the Corica Open Space Project, for providing our meeting space at the Corica Park Golf Course Clubhouse.
The Corica Park Open Space Project is devoted to building community by expanding access (for everyone) to the open space Corica Park occupies and sustains, creating opportunities that drive the success of our future leaders, and positively impacting friends, neighbors and community members. We are excited by all of the amazing opportunities presented by this community initiative and cannot wait to participate in, and offer you more activities and events to come!
We’d also like to thank ABM Computers for their donation of computer hardware to the Alameda Native History Project. This equipment will help us ensure that everyone has an opportunity to develop their maps skills through hands-on learning experiences.
We also want to acknowledge that your donations, and the proceeds from the Indigenous Bay BART Map sales have made it possible for us to do this.
Thank you for your continued support, can’t wait to see you at our Maps Class.
For more information on how to obtain a scholarship, or how to sponsor someone, please reach out to us directly at collab@nativehistoryproject.org.
Alameda Native History Project is fiscally sponsored by The Hack Foundation (d.b.a. Hack Club), a 501(c)(3) nonprofit (EIN: 81-2908499)

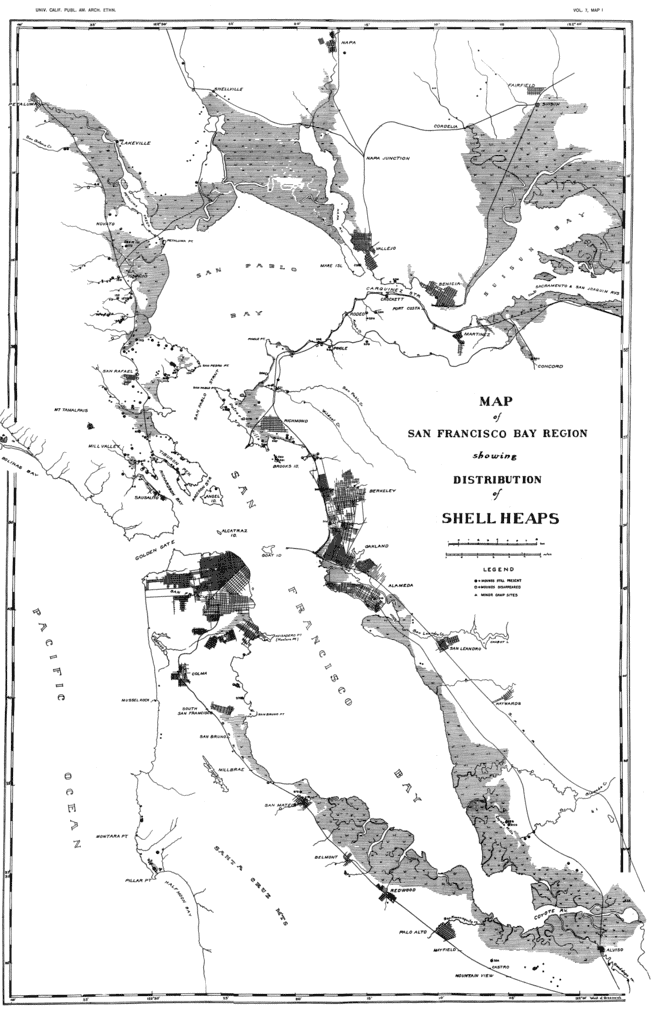
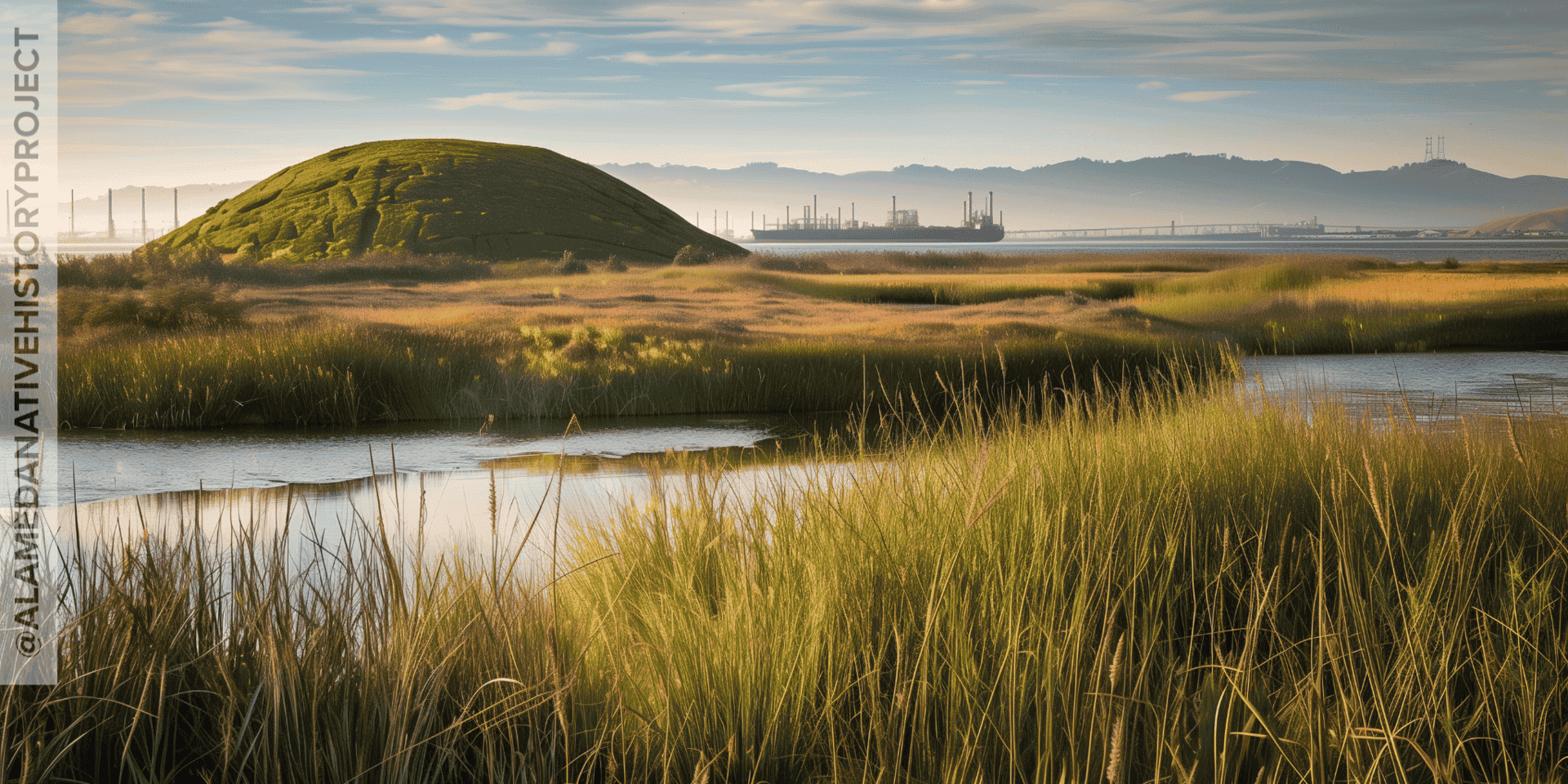
Despite the fact that shellmounds are cemeteries, hundreds were still destroyed all around the Bay Area.
And–to make matters unimaginably worse–the bodies inside were ground up, and used as overspread to level out train tracks, and build massive infrastructure (like the Angel Island Immigration complex.)
Even though some news stories feature witnesses who described bones disintegrating, or “turning to dust” as soon as they were handled…. People are still finding skeletons in places like Alameda, California, whenever they dig somewhere for the first time in a hundred years–which isn’t hard to do when many houses in Alameda are 100 years old.
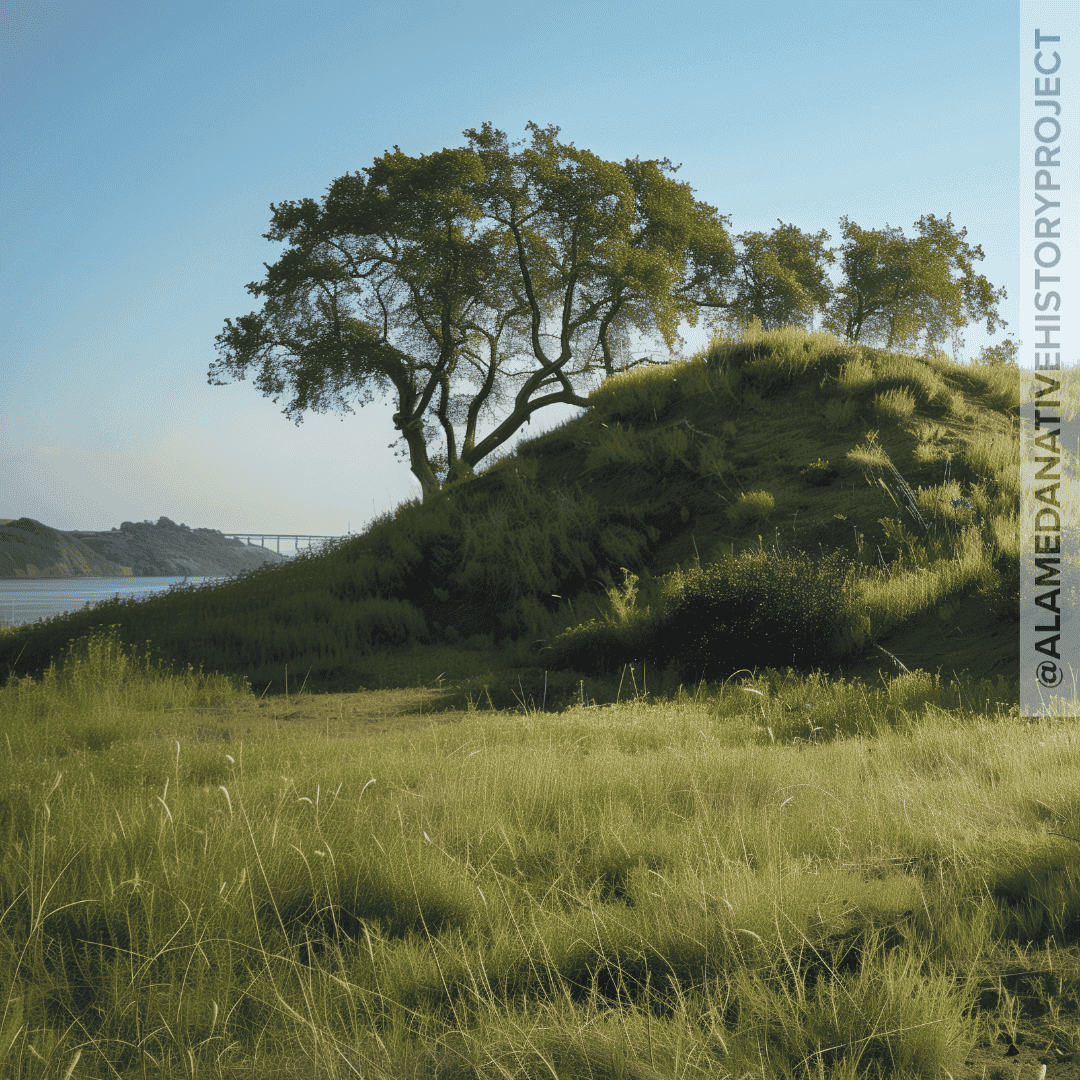
In spite of the desecration, and destruction visited on hundreds of shellmounds here in the San Francisco Bay Area, many still survive. And a surprising amount shellmounds survive intact.

This list includes (but is not limited to):





Obviously, much of this work was made easier by the dispossession, missionization, forced internment (on reservations), and annihilation, that Indigenous People endured since First Contact with Europeans.
It’s up to us to break the cycle of destruction. The cycle of purposely disconnecting people from the places they come from. And then destroying those places (literally) for no other reason than the speculative amount of value or resources the land is worth.

One of the ways we can put the earth back into balance is by letting those who are from this earth gain access to their ancestors; and traditional places (like hunting camps) and resources (like a river) which provide a tribal cultural benefit.
Traditional tribal hunting grounds provide a tribal cultural benefit as source of traditional sustenance…. A river (or certain parts of it) where fish are caught, or plants or other things are gathered, is a natural resource which provides a tribal cultural benefit.
There is an air gap between the idea of land stewardship as a Native American landscaping service; and land stewardship through traditional cultural practices which have shaped much of the natural ecosystems of the Bay Area for over 10,000 years.



Fundraising campaigns like “Shuumi Land Tax” take away from the real causes of Ohlone Tribal Recognition, Ohlone Tribal Sovereignty, and Ohlone Ancestral Land Back.
Ohlone people deserve respect and deference. When you give your land acknowledgment or money, do your research first. Don’t confuse non-profit corporations with actual tribes.
*The Shellmounds section of this website has more links to information.
Alameda Native History Project has remixed the San Francisco Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) System Map to show:
Travel the Indigenous Bay with Native Pride!

For real, though, once they run out, it’s going to be a minute before another run is printed. And you’ll be forced to make due with one of our other awesome maps.