
Fully updated, featuring new historic wetlands, shorelines, and more.
Available exclusively at the Alameda Native History Project.
Find it on our website:
NativeHistoryProject.org > Maps > Alameda Shellmounds Web Map
All juxtaposed against the modern day landscape to provide accurate scale and positioning.
Available in several sizes.

Because of the juxtaposition of the historic peninsula with it’s present day silhouette, it is much easier to see which parts of Alameda were physically connected and formed the peninsula more recently known as the “Encinal”.
Both Alameda and Oakland are in a region referred to as Xučyun (also known as “Huchiun”.) Xučyun is part of the ancestral homeland of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area. Muwekma have lived in the Bay Area for over 10,000 years.
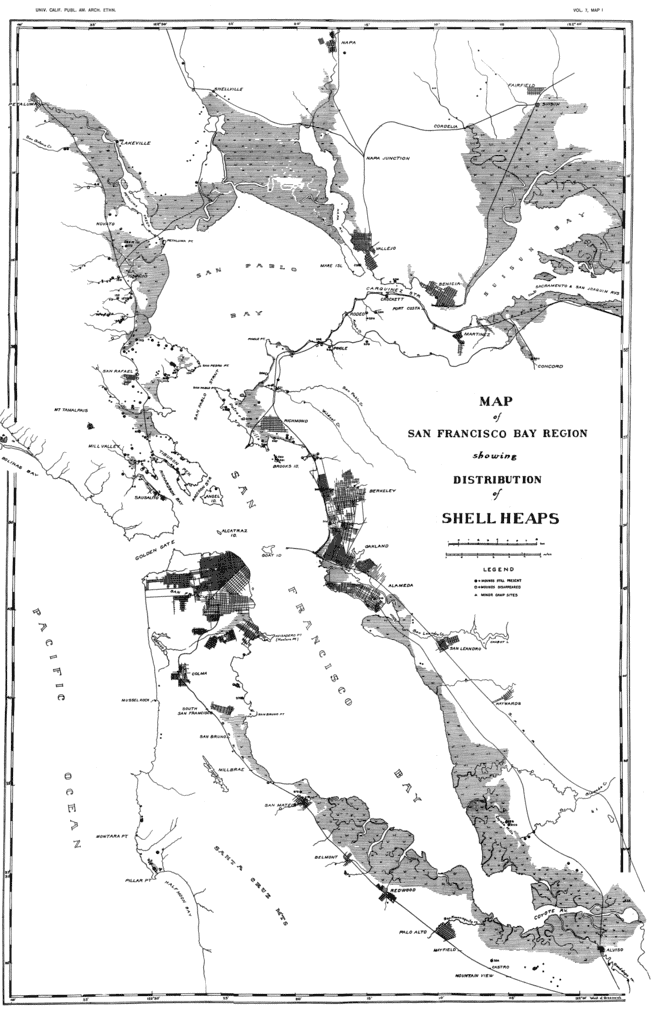
For the first time, all four of the Alameda Shellmounds have been put onto one map. Most people only know about the shellmound on Mound Street. But there are more shellmounds, in Alameda. There were over 425 shellmounds in the Bay Area. Including Alameda’s largest shellmound, at the foot Chestnut.
See also: Shellmounds – What Are Shellmounds?
This place we call Alameda was once called “La Bolsa de Encinal”. Meaning, “the Encinal forest”. Because the peninsula was host to a verdant, “ancient”, Live Oak forest. (The forest still exists. It just looks different.)
Many of the first accounts of the historic peninsula use rather idyllic, and paradisaic language to describe the rich pre-contact ecosystem that thrived here.
Alameda was once referred to as a “Garden City”. This is the place where the Loganberry was supposedly born.
tl;dr : Everyone wants to know where the landfill is. [There! I said it, okay?] They don’t even really care where Alameda used to be connected to Oakland. Or about the ancient whirl pool in la bahia de san leandro. But, whatever.
Look closer, and you can see the footprints of present day buildings. That’s the landfill.
For real though, I made this layer using pre-1900 shoreline vector data I compiled for the Bay Area region, and stitched together.
In Version 1, I made a kind of sloppy polygon with historical shoreline vectors, and painted it green. It was a good placeholder for the historic marshes and wetlands of the Bay Area.
Version 2 features the finely detailed historic wetlands layer created for the Bay Area Shellmounds Maps. It features very precise cut-outs for historic creeks, channels and waterways; and features full-coverage of the Bay Area region.
If you want some actual historical eco-data, check out the San Francisco Estuary Institute. They have some brilliant historical ecology GIS you would probably love, if you’ve read this far.
The Alameda Shellmound Map, Version 2, is ground-breaking in its completeness and exquisite detail.
Printed in vivid color, on premium paper. Purchase through the Alameda Shellmounds Map square payment link. 10% of all proceeds from Alameda Shellmounds Map sales go to the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area.

[Footnote: Imelda Merlin mentioned numerous shellmounds in her Geology Master Thesis, but none of her assertions were backed up with any relevant citations. And geology is not archaeology, ethnology, or anthropology, the areas of study that normally concern themselves with Tribal Cultural Resources like shellmounds.
Furthermore, the famous “Imelda Merlin Shellmound Map” was actually a map of Live Oak trees present in Alameda at the time Merlin wrote her thesis (in 1977).
The “Map of Whitcher’s Survey of ‘The Encinal’ in 1853. In Alameda City Hall.”, cited on page 104 of Merlin’s thesis, has never been found by Alameda City Hall, the Alameda Free Library, or the Alameda Museum.
Certainly this means Imelda Merlin has failed to meet the burden of proof required for institutions like Alameda Museum to take reliance upon her claims re: Whitcher’s Survey, and locations of any mounds. Yet, somehow, Merlin’s geology thesis was Alameda Museum’s sole reference regarding shellmounds. (For years Imelda Merlin’s geology thesis was viewed as the authoritative source of information about Alameda shellmounds.)]
One of the ways Alameda Native History Project decolonizes history is by interrogating the record. This means tracking down and reading citations. Critically evaluating reports and studies for bias. And calling out poor research, and prejudiced conclusions for what they are.
We decolonize history by updating the maps and diagrams of our past. Producing accurate, fact-based educational and reference materials to replace the biased and inaccurate educational products–which are still misinforming our schoolchildren and the greater public today.
By providing a more nuanced and comprehensive perspective; and doing away with the old, over-copied handouts from decades past: we are able to shed the misinformed, and racist, stereotypes and quackery that typify generations which brought us things like: “kill the indian, save the man”, Jim Crow, and “Separate But Equal”.
We vigorously challenge the cognitive dissonance of so many California Historians, asking “Where did all the Indians go?”, at a time when the entire United States had declared war on Native Americans. … Including the first Governor of California, who called for “war of extermination” against California Native Americans.
These ideas, stereotypes, attitudes, and beliefs have managed to propagate themselves time and time again in the textbooks and lesson plans used to “educate” countless generations of Americans.
👉🏼 Your purchase of the Alameda Shellmound Map supports our mission of decolonizing history. 🙌🏼

Despite the fact that shellmounds are cemeteries, hundreds were still destroyed all around the Bay Area.
And–to make matters unimaginably worse–the bodies inside were ground up, and used as overspread to level out train tracks, and build massive infrastructure (like the Angel Island Immigration complex.)
Even though some news stories feature witnesses who described bones disintegrating, or “turning to dust” as soon as they were handled…. People are still finding skeletons in places like Alameda, California, whenever they dig somewhere for the first time in a hundred years–which isn’t hard to do when many houses in Alameda are 100 years old.
In spite of the desecration, and destruction visited on hundreds of shellmounds here in the San Francisco Bay Area, many still survive. And a surprising amount shellmounds survive intact.

This list includes (but is not limited to):





Obviously, much of this work was made easier by the dispossession, missionization, forced internment (on reservations), and annihilation, that Indigenous People endured since First Contact with Europeans.
It’s up to us to break the cycle of destruction. The cycle of purposely disconnecting people from the places they come from. And then destroying those places (literally) for no other reason than the speculative amount of value or resources the land is worth.

One of the ways we can put the earth back into balance is by letting those who are from this earth gain access to their ancestors; and traditional places (like hunting camps) and resources (like a river) which provide a tribal cultural benefit.
Traditional tribal hunting grounds provide a tribal cultural benefit as source of traditional sustenance…. A river (or certain parts of it) where fish are caught, or plants or other things are gathered, is a natural resource which provides a tribal cultural benefit.
There is an air gap between the idea of land stewardship as a Native American landscaping service; and land stewardship through traditional cultural practices which have shaped much of the natural ecosystems of the Bay Area for over 10,000 years.



Fundraising campaigns like “Shuumi Land Tax” take away from the real causes of Ohlone Tribal Recognition, Ohlone Tribal Sovereignty, and Ohlone Ancestral Land Back.
Ohlone people deserve respect and deference. When you give your land acknowledgment or money, do your research first. Don’t confuse non-profit corporations with actual tribes.
*The Shellmounds section of this website has more links to information.
Alameda Native History Project has remixed the San Francisco Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) System Map to show:
Travel the Indigenous Bay with Native Pride!

For real, though, once they run out, it’s going to be a minute before another run is printed. And you’ll be forced to make due with one of our other awesome maps.
The Alameda Native History Project is proud to announce their Cultural & Educational Program Offerings for 2024-2025.

The challenge is creating something that will withstand the elements over winter.
We will meet as a team to construct these Acorn Granaries. Together we will learn about the different kinds of Acorn Granaries; integrated pest management uses of California Native Plants; and how indigenous technology works to keep food safe for centuries.
This is a series of free events which happens 10am-2pm Every Sunday in July.

Learn about the ancient Live Oak Forests of this place now called “Alameda”. Learn about the nutritional value and the cultural significance of acorns.
There are a number of different ways in which everyone can participate. Please check out the list of roles available on the Sign-Up Form, right after our Community Guidelines.
Snacks, Water, Coffee, and Lunch, will be provided.

Sample traditional Acorn Mush.
Make different baked goods using Acorn Flour made from Alameda Oak Trees. Leave with your own Acorn Flour, and recipes to try at home!
This session is Free!
Muwekma Ohlone Tribal Recognition Process
US DOI Bureau of Indian Affairs, Petition #111 Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of San Francisco Bay, CA
Muwekma Tribal Publications (Research Documents)
Featuring articles by Les Field, Alan Leventhal, and more.
This is not a complete list of sources. For instance, the California State Universities are another source for information not listed here–even though Alan Leventhal is associated with the CSU system. This is just a selected list of some resources to get you started.
If you find other resources for primary and secondary materials which are not listed here, please let us know.
Right now, we’re in the process of finding and compiling local archival sources.
If you are an individual or organization who also keeps their own libraries and collections regarding this subject, or Native Americans in the San Francisco Bay Area, and you would like to share, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Hopefully, when you read this, you already know that Shuumi Land Tax doesn’t really go to all Ohlone people. (But we don’t want to discourage your well-meaning intent and your need to help Indigenous people in anyway you can.)

The Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area
This is the real Ohlone tribe you probably thought you were donating money to when you considered paying Shuumi “Land Tax”.
With over 10,000 years of continuous habitation of this place now known as the San Francisco Bay Area, your donation directly to this tribe of over 600 enrolled members will be felt immediately; and put to use as Muwekma reawaken their Chochenyo language, remember dances, and revitalize their culture.
The Muwekma Ohlone Tribe is a bonafide native American Tribe, which has been recognized over and over again by The Courts, but still struggles for recognition with the Bureau of Indian Affairs. Muwekma is set to begin their Trail of Truth in their epic battle for justice; in the form of a Tribal Homeland, Education, Housing, Medical Services, and–last but not least: Sovereignty.
If you want to help Ohlone people in the San Francisco Bay Area (and beyond):
Go to Muwekma.org to educate yourself and your friends about the Indigenous People of the San Francisco Bay Area.
[See also: “Who/What/Where is Lisjan?“, “Who are the Lisjan Ohlone? What does Chochenyo mean?”, “Corrina Gould Convicted of Fraud“]

Intertribal Friendship House Oakland
Established in 1955 as one of the first urban American Indian community centers in the nation.
It was founded by the American Friends Service Committee to serve the needs of American Indian people relocated from reservations to the San Francisco Bay Area.
“The Bay Area American Indian community is multi-tribal, made of Native people and their descendants—those who originate here and those who have come to the Bay region from all over the United States and from other parts of this hemisphere.“
IFH Oakland’s local programming is important and impactful.

Friendship House SF
Friendship House SF provides a girth of wellness services for Native American People in the SF urban rez.
One of the most important services the Friendship House SF provides is treatment and recovery services for Native Americans. Lots of tribes will send their members to the Friendship House SF for their treatment and recovery services.
The Friendship House SF also provides meeting space for other organizations to hold their events and retreats. Very thankful to the Friendship House SF for giving me and organizations I’ve been a part space for so many years.

Native American Health Center
Provides primary care, mental health, and dental services primarily. Also organizes and hold the Indigenous Red Market, contributes to Powwows, and other Native American Events and Programs throughout the San Francisco Bay Area.
Contributing to this organization will also support a wider range of programs and services in the Bay Area.
NAHC is a pretty solid choice, all around.

American Indian Cultural Center
A member of Intersection for the Arts.
Since 1968, the purpose of the American Indian Center has been to create a community space based on Native American values, culture, programming, traditional foods, and community support.
Contributing to this organization will help sustain AICC’s mission to improve and promote the well-being of the American Indian community and to increase the visibility of American Indian cultures in an urban setting in order to cultivate awareness, understanding and respect.

American Indian Child Resource Center
The American Indian Child Resource Center is a non-profit social services and educational community-based organization serving American Indian community members from across the greater Oakland/San Francisco Bay Area and surrounding counties.
The American Indian Child Resource Center is a COA Accredited Organization.

First Nations Development Institute
Economic Development Corporation which invests in and creates innovative institutions and models that strengthen asset control (land stewardship is one example) and support economic development (through grants and programs) for American Indian people and their communities.
First Nations Development Institute is another solid choice because you know your money will be well invested, and you can read the reports on how it was used.





P.S.
You can always donate to the Alameda Native History Project, or any of these other organizations, any time of the year! Don’t wait until Thanksgiving.
By now there should be no doubt that most museums, which display or hold Native American artifacts, directly benefit from grave robbing, or the often racist, prejudiced language and ignorant beliefs regarding Native Americans first uttered by now dead anthropologists [like Alfred Kroeber], and perpetuated by the ailing volunteers and aging septuagenarians responsible for interpreting and curating these artifacts today.
Many of these museums do no care to get the information or facts straight, and continue to present California Native Americans as “extinct”, “disappeared”, and brush off or dismiss any mention of actual living Native people as someone trying to raise trouble.
Advocates for the truthful portrayal, accurate naming, and return of tribal objects and remains are often called “hostile”, dismissed as rabble rousers, and subjected to projection by the very people who should have read White Fragility.
Even more infuriating is the belief consulting with any Native American individual on any subject–whether or not it’s related to the stolen Tribal Grave Goods or Ceremonial Objects in these Museum’s possession–is used as cover for the Museum to continue to disregard the wishes of the very real, and still living Native American people who have a lawful claim, and a legal right to demand the return and repatriation of these Native American Tribal Resources and Cultural Objects.
In fact, many of the people museums choose to consult with regarding Native American artifacts are not Native Americans at all.
Truthfully, Native American people are consistently shut out of events, exhibitions and lectures about their own culture and identity.
A lot of apologists will say “it’s not like this anymore”; or dismiss the Standard Operating Procedures museums as a thing of the past…. But these conditions till persist.
Native American People continue to be discounted, ignored; and their history, culture and contributions continue to be minimized and ignored.
But the truth remains: The artifacts and objects on display in most museums have been stolen from Native American People, their graves, and do not belong to the museums who refuse to return them.
It’s a shame that these institutions are unwilling to do the research and work necessary to properly identify Tribal Cultural Objects and Native American Remains to repatriate the same way they did the research to identify and prepare the same goods and burials for exhibition.
It’s despicable the way Museums claim such helplessness and ignorance when it comes time to give stolen objects back, even though the exact same objects are the she subjects of fundraising events and lectures proudly given by white anthropologists, and non-native experts, even today.
Charlene Nijmeh, the Chairwoman of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area, talks about how the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe was removed from the rolls of Native American Tribes simply for the purpose of denying Ohlone people in the San Francisco Bay Area their right to a tribal land base; because land in the Bay Area is so valuable.
In this same way, institutions like the University of California Berkeley (which holds the remains of thousands of Native Americans) are incentivized to claim an inability to identify which tribes the bodies in their crypt belong to.
So, too, are Museums incentivized to weaponize their incompetence in order to keep their pilfered goods.

This is a completely reprehensible argument that bears no merit, as far as I’m concerned. Simply because these same people would not agree that their family members are more valuable being dug up, defiled in the name of science, and put on display without so much of a whisper of their name or life’s story.
The blatant disrespect of Native American Graves as things which can be dug up, broken, moved to a landfill, reburied, and used as overspread is something which has been enabled by the statements of people like Alfred Kroeber, who explicitly declared entire tribes of Native Americans (like Ohlone people) “extinct”.
It s because these remains are considered “ancient”, or attributed to a time before our modern history where no living descendants exist–“pre-historic” for all intents and purposes–that oil companies, city, state and federal governments have dug up the bodies of our ancestors with impunity. And why money is still being given to universities to study our ancestors’ remains, even today.
But this is a fallacy, because Native American people are not extinct; they have not disappeared. We are still here, today. And we do not want anyone digging up our relatives to build pipelines, parking lots… or “for science”. Period!
(How come laws against the abuse of a corpse apply to every body except for Native American bodies?)
Museum Fallacy #3:
“If we give away all of our artifacts, we won’t have any left!”
“If we give away all of our artifacts, we won’t have any left!” This was actually said to me by a volunteer at the Alameda Museum.
This is dissonant because many museum’s holdings are made of stolen property. Repatriation is the only correct course of action; anything less is a travesty.
This standing also presumes the only thing of value the museum has to offer is the exhibition of original artifacts, no matter how broken or uninteresting those artifacts are; and, in spite of the fact that curators and museum staff and volunteers have no […] clue how those objects are used, where they actually came, or what the history of their use and development is.
In all of this, there is not even a hint of concern about whether or not the museum has a duty to investigate/research, find, and try to contact the tribe associated with the Native American objects and artifacts in their possession.
Consideration of actual Native American People is so far removed from the discussion, it’s a little ridiculous.

Especially given the fact that these Museum are inviting Native American people to give lectures during Native American Heritage Month. (But consider the audience….)
The idea that there aren’t enough artifacts is a fallacy based upon a false sense of ownership and authority magically imbued by the mere possession of these stolen grave goods.
The implied scarcity mindsight that the only thing which gives museums like the Alameda Museum any value is a handful of broken pieces of bones and tools–which no one knows the use for (or even the names of)–is laughable in its appeal to ignorance.
The fact that Alameda Museum is not, and has never been, the place to see Native American artifacts belies this mindset as a straw man argument for the lack of interest or determination of the museum to change or do any better. But, in the end, it’s the museum which must do the work.
Indigenous science is a distinct, time-tested, and methodological knowledge system that can enhance and complement western science. Indigenous science is about the knowledge of the environment and knowledge of the ecosystem that Indigenous Peoples have. It is the knowledge of survival since time immemorial and includes multiple systems of knowledge(s) such as the knowledge of plants, the weather, animal behavior and patterns, birds, and water among others.
Museums will do well to remember these facts when treating Indigenous People with the reverence and respect they deserve.

Truthfully, the reason why this policy was set was mostly out of respect for the lived experiences of the Tribal Members of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe of the San Francisco Bay Area.
And as a direct response to the continuing tokenization and empty promises of non-indigenous corporations, governments, and individuals who seek to monetize the appearance of Indigenous People at their events, solely for the exclusive benefit of the hosting organization/corporation.
And, while people like Corrina Gould are more than happy to take a check for their appearance, and play the part of a Tribal Chairperson; the real Indians–bona fide Native Americans–actual, self-respecting Indigenous People–will likely never respond to these invitations.
I mean… really… how do “well-meaning”, “progressive”, non-indigenous people manage to come up with more and more ritually ridiculous ways to re-traumatize a group of people they tried to murder, and wipe off the planet?
And they think letting us tell them they’re thieving, murderous interlopers is doing us a favor? No, Land Acknowledgments are yet another song and dance indigenous people are being expected to perform (for free) to put white people at ease.
Mind you, every interaction with white people during the “Discovery Era” was exploitive and extractive; and, of course, only benefitted the colonizer with free food, riches, labor, etc.
It’s important to note the similarities between the intent of both Aboriginal Australians, and Indigenous, and First Peoples of the Americas, when meeting newcomers.
Veritably, the white-washed version of the “discovery” and “founding” of America includes references to the “First Thanksgiving” as a celebration of how Native people “helped” white people to survive a place these Colonizers knew nothing about, and would have perished in, if left on their own.
The clean, anesthetized, version of White History yields so many selfless examples of Indigenous generosity and kindness.
And demonizes the audacity of indigenous people who object to the taking of their land, destruction of their resources, and kidnapping, enslavement and abuse, and murder, of their people.
It’s all so guilt free.
White History carries with it a sense of smugness and blamelessness, which purports to release all white people, all colonizers (and their descendants), of the liability for their damages, ill-doings, and complicity, in what today are called War Crimes, and Crimes Against Humanity….
And, even more worse than that: when indigenous people give headdresses out to people like The Pope: it really signals absolute forgiveness for something which white people haven’t even begun to admit to, much less atone for; and releases them from the burden of ever performing a genuine confession, reconciliation and/or atonement.
When pressed, organizations will fess up pretty quickly:
“We didn’t invite you here to acknowledge the wrong-doings of our ancestors, or the continuing injustices against Native Americans we commit, or are complicit in….
“We really just wanted someone with shell jewelry and feathers to burn sage, give a blessing–and play the part of what we believe an idealized Native American should look like, so we can check that box on our Diversity Equity and Inclusion component for this year….
“We didn’t actually mean to do any work.“